On September 26, 2024, as Hurricane Helene battered Florida’s Gulf Coast, it produced vital storm surges, impacting quite a few communities throughout the area. Throughout this excessive climate occasion, NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE), stationed aboard the Worldwide Area Station, noticed gravity waves within the ambiance roughly 55 miles above Earth’s floor. This knowledge, gathered as a part of NASA’s research on area climate, goals to make clear how terrestrial climate impacts technological methods resembling satellites and communication networks.
Observations from NASA’s AWE Instrument
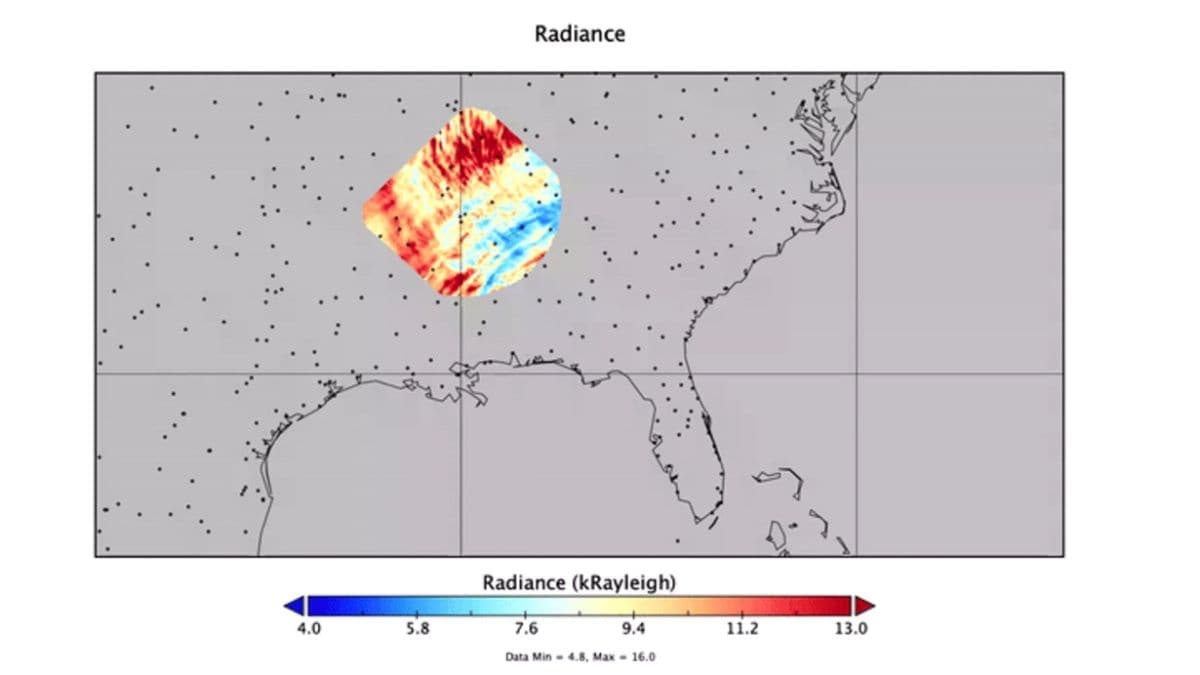
Because the Worldwide Area Station crossed the southeastern United States, the AWE instrument recorded massive concentric waves within the ambiance, originating from the extraordinary circumstances stirred by Hurricane Helene. These gravity waves, which seem as artificially colored bands in purple, yellow, and blue, depicted adjustments in radiance inside the Earth’s mesosphere. The imagery, enhanced with color to focus on infrared brightness variations attributable to airglow, captured waves stretching westward from northern Florida.
Significance of Atmospheric Gravity Waves
In line with Ludger Scherliess, Principal Investigator of NASA’s AWE at Utah State College, the waves resemble the ripples produced when a pebble hits the floor of a pond. The instrument, launched in November 2023, was designed to determine these atmospheric disturbances, which embody storms, hurricanes, and different violent climate occasions that trigger gravity waves. The evaluation of such atmospheric adjustments, produced throughout turbulent climate, offers important insights into how terrestrial occasions affect circumstances in area.
Analysis Implications for NASA
The gravity waves from Hurricane Helene are among the many first photos launched to the general public by the AWE mission. Via these observations, NASA seeks to know how Earth’s climate methods influence the higher ambiance and area climate. The AWE instrument’s capacity to detect these disturbances contributes to ongoing analysis, enhancing NASA’s efforts to evaluate the potential disruptions to Earth-orbiting methods.